The term software sales is an umbrella term for the various sales roles involved in selling software products to other businesses. It’s a growing and lucrative industry to be in, and the companies are known for offering high salaries, top-of-the-line benefits, flexible working hours and location, and fun, fast-paced company cultures.
The term software sales is an umbrella term for the various sales roles involved in selling software products to other businesses. It’s a growing and lucrative industry to be in, and the companies are known for offering high salaries, top-of-the-line benefits, flexible working hours and location, and fun, fast-paced company cultures.
Today we’ll tell you everything you need to know about tech sales, including the following:
- Why you might consider working in the field.
- The types of software sales positions, their average earnings, and their responsibilities.
- The types of software companies you can work for (Medical software, RE software, etc)
- The best software companies are almost always hiring sales reps.
- The best cities for software sales (#1 is remote work).
Let's find out more in this software sales ultimate guide. But before we go into what it’s like working in software sales, let’s give a textbook definition of the term.
What is Software Sales?
Software sales is a career field composed of salespeople that sell software products, primarily to other businesses. The field encompasses a wide range of job titles, from entry-level positions like Business Development Representative to experienced positions like Enterprise Account Executive or VP of Sales.
There is an equally diverse range of software products that these salespeople sell, from legal and HR software to construction and cyber security tech. Recognizable companies like Salesforce, Microsoft, HubSpot, and Oracle all fall under the category of software companies.
Why Work in Software Sales?
As software companies continue to pop up left and right, the demand for tech sales reps continues to grow. Because of the high demand and profitability of many software products, sales reps in this industry enjoy high compensation, a flexible work environment, and countless growth opportunities. Companies, especially startups, are intent on keeping their sales talent happy.
High Compensation
Software sales reps have high earning potential when compared to salespeople from other industries. The average base salary for software sales representatives is $63,753, according to 3,800+ reported salaries on Glassdoor.
However, this number is only part of the picture. It excludes other common components of a software sales rep’s compensation, such as commission and bonuses, which can easily bring your earnings up to six figures.
With the right product and work ethic, a software sales rep can earn a beyond satisfactory amount of money. That’s the beauty of sales. To a greater extent than most other jobs, your earnings are attached to your individual performance.
Because of this, a first-year Business Development Rep who hits 150% of their quota can easily hit $100,000 in total earnings. Of course, earnings depend on factors like your title, company, and skill.
As a rule of thumb though, pay gets better as you move up the ladder. Take a look at these base salaries for top Account Executives. Keep in mind the numbers exclude commission, which is usually about equal to base salary, meaning these rep’s total earnings are likely about double what’s listed below.
Flexible Lifestyle
Software companies are notorious for offering lots of vacation time, flexible working hours, remote work opportunities, and other perks that enable you to live life the way you want. While quotas can be demanding at certain companies, as long as you’re able to hit them, your manager will usually allow you a great extent of autonomy.
Not to mention, many software companies, especially startups, make their work environments as enjoyable as possible, filling them with anything from a ping pong table to a fully stocked bar.
There’s something special about sipping a frothy pint at your office while the CEO walks past and waves hello. Plus, if you overindulge and trip on the sidewalk, you’ll likely have amazing health benefits to cover your medical expenses. Software companies are known for their excellent benefits for health coverage, dental, parental leave, and more.
Growing Field
The software industry continues to grow at a fast rate, making tech sales acumen a great thing to add to your skillset. Those skills will be more and more marketable and valuable as the industry grows.
Below is a graph demonstrating the expected growth rate of the software industry in the US, broken down by software type:
Here are some stats about the software industry and its growth:
- Business software (including most companies software reps work for) is expected to have a compound annual growth rate of 11.3% from 2021 to 2028.
- Software market revenue is projected to hit US $581,184m in 2021, according to Statista.
- 28,051 people work in software sales according to Zippia.
To put the software industry’s growth in perspective, the projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the financial services industry was 2.8% from 2016 - 2021, and the growth rate for the legal industry is projected at 4.9% CAGR from 2020 - 2025. Both are less than half of the growth rate of the software industry.
Now, let’s jump into the different types of sales jobs and career paths you can have in the software sales field.
Types of Tech Sales Jobs and Career Paths
There are many different types of software sales jobs, each with its own average compensation, set of day-to-day responsibilities, and potential career path, and each demanding certain qualifications and skills.
The seven most common job titles in tech sales are as follows:
- Business/Sales Development Representative: Focuses on outbound prospecting to book meetings or demos for Account Executives.
- SMB Account Executive: Responsible for managing and closing deals with prospects from small and medium-sized businesses.
- Mid-Market Account Executive: In charge of managing and closing deals with prospects from mid-market companies.
- Enterprise Account Executive: Responsible for strategically closing sales deals with large businesses.
- Sales Management: Consists of Directors of Sales, VPs, Mid-level managers, and any other role that directly manages software sales professionals.
- Solutions Consultant/Engineer: Tasked with determining the operational and technical scope of a business opportunity and presenting it to prospects.
- Customer Success Manager: Manages the relationship with clients post-sale and helps them use the software effectively.
Tech sales’ wide variety of positions makes the field potentially satisfying to almost any personality type. For example, someone very interested in how technology works would enjoy being a solutions consultant for a complex software platform. Meanwhile, someone competitive who loves building relationships would derive much pleasure from the role of an Account Executive.
Below we’ll describe each position and share their average earnings, responsibilities, and career paths. Plus, we’ll tell you the basics of what qualifications you need to get the job.

Sales Development Representative/Business Development Representative
A sales/business development representative (S/BDR) is responsible for opening sales opportunities with new accounts. They do this primarily by outbound prospecting: cold calling, emailing, social selling, etc, but they might also attend in-person events or tap into their network.
This is a classic entry-level position in the field of software sales. It’s where many VPs of Sales and Enterprise Account Executives learned the ropes.
Here’s the breakdown of the software sales development representative experience:
- Responsibilities: Prospecting for new leads, qualifying inbound and outbound leads, setting introductory meetings or demos with qualified leads, and updating CRMs.
- Average Earnings: $49,937 average annual base salary. Senior SDRs can expect to earn $54,496 base salary. The average variable annual compensation is $10,000-20,000k (outside NYC and Bay Area, which typically offer higher pay).
- Potential Career Paths: SDRs typically advance into sales management positions (perhaps managing SDRs) or into a closing Account Executive role, where they enjoy higher earnings.
- Preferred Qualifications: Some companies require college degrees. Others don’t. Some require prior sales experience. What they’re really looking for though is someone persistent, good at talking to people, and entrepreneurial.
- Required Skills: Cold calling skills, cold emailing skills, comfortable on the phone, able to learn technology quickly.
Being an SDR or BDR is a great way to build your knowledge about a company’s product as well as sales in general. It’s best for those with competitive and resilient spirits, as rejection will be a constant occurrence for those on the job.
But that’s a blessing in disguise. That constant cycle of getting rejected and trying again teaches you resilience in the face of adversity. It teaches you to go after what you want, even if the road leading there is scary and uncomfortable.
SMB Account Executive
An SMB Account Executive sells software solutions to small and medium-sized businesses, defined as companies employing between 1-1000 employees. AEs typically manage the sales processes from the introductory meeting to the signed contract.
To do this they typically hold discovery calls with decision-makers, host web demos of the software, handle objections, and craft and send business proposals and/or contracts. Sometimes they’ll be in charge of their own prospecting, but usually, they’ll enjoy the luxury of an SDR setting meetings.
Here’s a glance at the SMB Account Executive experience:
- Day-to-Day Responsibilities: Managing a pipeline filled with different accounts, giving web demos, giving in-person presentations, handling objections, negotiating terms, and closing the sale.
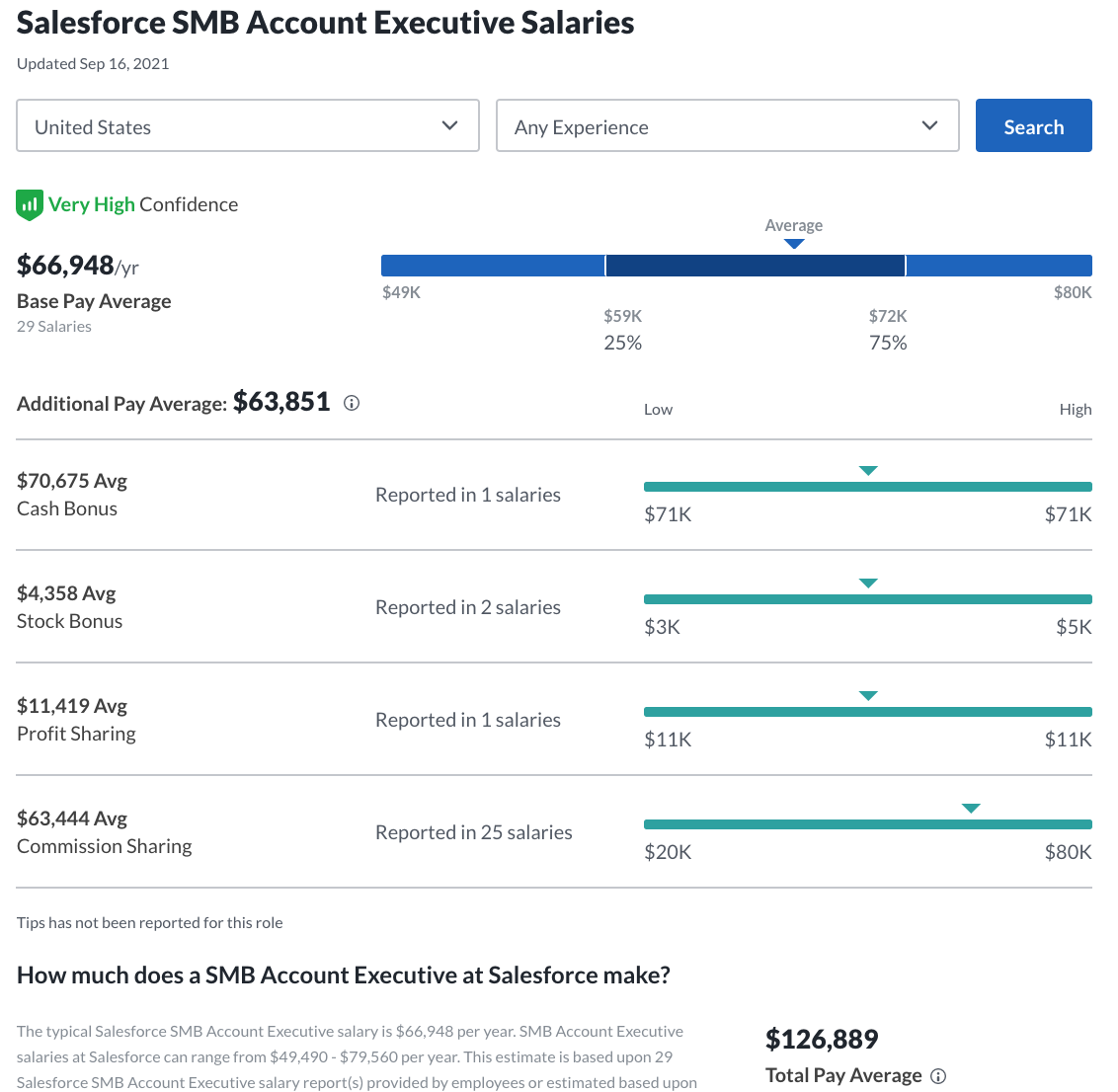
- Average Earnings: $56,507/yr base salary. Typically commission will represent 50% of an SMB AE’s on-target earnings, so if they hit their quota they’ll earn over $100,000/yr.
- Potential Career Paths: They’ll typically move up the ladder to close bigger deals as a Senior Account Executive or Mid-Market Account Executive.
- Preferred Qualifications: Experience with SaaS systems and B2B sales. A track record of consistently meeting revenue quotas. 2+ years as a quota carrying rep. Experience giving web demos.
- Required Skills: Relationship builder, quick learner, problem solver, hunter, closer.
If you become an SMB Account Executive for a successful company with an in-demand product, you’ll have the opportunity to bring in a lot of money. For example, Salesforce’s SMB AEs make on average on-target earnings of $126,889/yr. Below is the breakdown of the payout:
Mid-Market Account Executive
A Mid-Market Account Executive sells software to mid-market companies, which are defined as having a market capitalization valued between 2 and 10 billion dollars and employing between 2,000 and 5,000 employees.
The Mid-Market Account Executive is responsible for managing full sales cycle deals that have slightly longer sales cycles than SMB deals.
Here’s a snapshot of the Mid-Market Account Executive experience:
- Day-to-Day Responsibilities: Managing deals, giving web demos, giving in-person presentations, handling objections, negotiating terms, sending contracts, closing the sale, updating CRM.
- Average Earnings: $75,891/yr base salary. Typically commission will represent 50% of an AE’s on-target earnings, so if they hit quota they’ll earn over $140,000/yr.
- Potential Career Paths: They’ll typically move up the ladder to close bigger deals as an Enterprise Account Executive.
- Preferred Qualifications: Background in software and B2B sales. A record of consistently meeting revenue quotas. 4+ years as a quota carrying rep. Experience giving web demos and juggling multiple deals. Closing experience.
- Required Skills: Relationship builder, problem solver, strong planning skills, strong communication skills, closing skills.
This position is a bit more challenging than the SMB AE position, for it forces reps to convince more than one decision-maker of the value of their product. Plus, since the deal sizes are larger, the monetary commitment for the buyer is higher, which always results in a tougher sell.
Enterprise Account Executive
Enterprise Account Executives have to close deals with large companies, typically with multiple decision-makers. The sales cycles are therefore usually long (sometimes 6-12 months) and the seller’s approach is typically more personalized and strategic than when selling to smaller companies.
Not only does the Enterprise AE have to convince them of the value of the solution, but since large companies often have complicated and rigid internal processes, this AE must also accomplish the often difficult challenge of figuring out how the software can fit into their business. The combination of difficulty and high revenue deals makes it the highest paying closing role in the software industry.
Here’s a snapshot of the software Enterprise Account Executive experience:
- Day-to-Day Responsibilities: Strategizing on how to move deals forward, talking on the phone with decision-makers, giving web demos, meeting buyers in person, updating CRMs, and negotiating contracts.
- Average Earnings: $110,718/yr base salary. And that’s just the base. Although we don’t recommend it. you could close no deals and walk away making 6 figures that year. If you hit quota on the other hand, you’re likely earning over $200,000/yr.
- Potential Career Paths: Many software Enterprise AEs will continue improving in their role and making more money, or they’ll switch companies for a better deal. They might also go into sales management positions.
- Preferred Qualifications: B2B sales and software experience. 6+ years as a quota carrying rep. History of surpassing quotas.
- Required Skills: Consultative selling, opening deals strategically, giving web demos, closing, building relationships over long sales cycles, and listening.
This position can be extremely demanding, but also extraordinarily rewarding and interesting, especially if you like to spend time talking with leaders of large companies to help them solve their problems with technology.
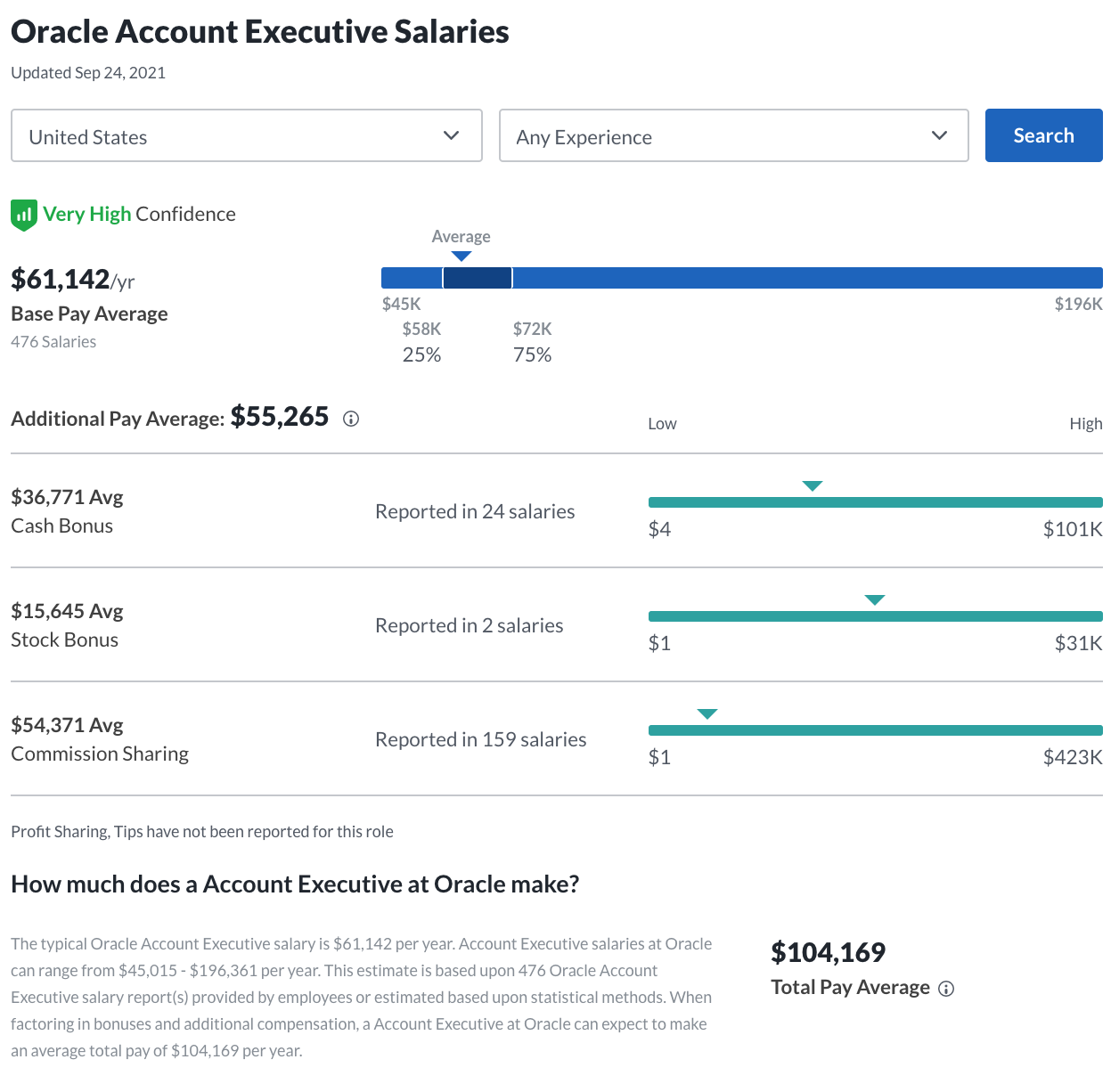
Here’s a glance at the base salaries some software companies are paying their Enterprise AEs:
Sales Management
There is a wide variety of sales management positions in software sales. Generally, there are three overarching levels of management, ascending in the hierarchy — Sales Manager, Director of Sales, and VP of Sales. In most software companies, these managers will not have selling responsibilities. They’ll focus on building and optimizing their sales teams.
Before going into the relationships between each level of management and their responsibilities, let’s check out their average base salaries below. Keep in mind that management can also make earnings in the form of commission sharing and bonuses.
- BDR Sales Manager: 84,331/yr average base salary.
- AE Sales Manager: $103,479 /yr average base salary.
- Director of Sales: $129,658/yr average base salary.
- VP of Sales: $167,893/yr average base salary.
The first tier in the management hierarchy, the Sales Manager, typically directly manages and coaches AEs or BDRs, ensuring they have all the support they need to hit their daily and monthly sales targets.
In a smaller company, the manager might double as and hold the title of Director of Sales, who is in charge of creating a sales plan, setting sales targets, and assisting in closing deals for a certain sales department, whether it be mid-market or enterprise deals.
In larger software companies a Director of Sales will manage a team of sales managers, perhaps in a certain region or sales type. For instance, they might be the Director of Mid-Market AEs. These Sales Directors will typically report to a VP of Sales, the grand-daddy of sales positions, who runs the entire sales department.
VPs handle a lot of the big picture work that drives the sales organization. They coordinate with other departments. For example, they’ll meet with marketing to ensure department alignment, and they’ll meet with customer success to look for cross-selling opportunities.
The VP might also head up the recruiting and interviewing process for new sales talent. They’ll set up onboarding plans to make sure those new hires are up to speed quickly, and they’ll regularly meet with Sales Directors or Managers to dissect and analyze the pipeline.
They also must be well-versed in sales metrics and reporting, as they’ll be expected to create forecasts that they’ll show to C-suite execs or the board of directors. Lastly, the best VPs participate in hands-on training and strategizing with sales reps.
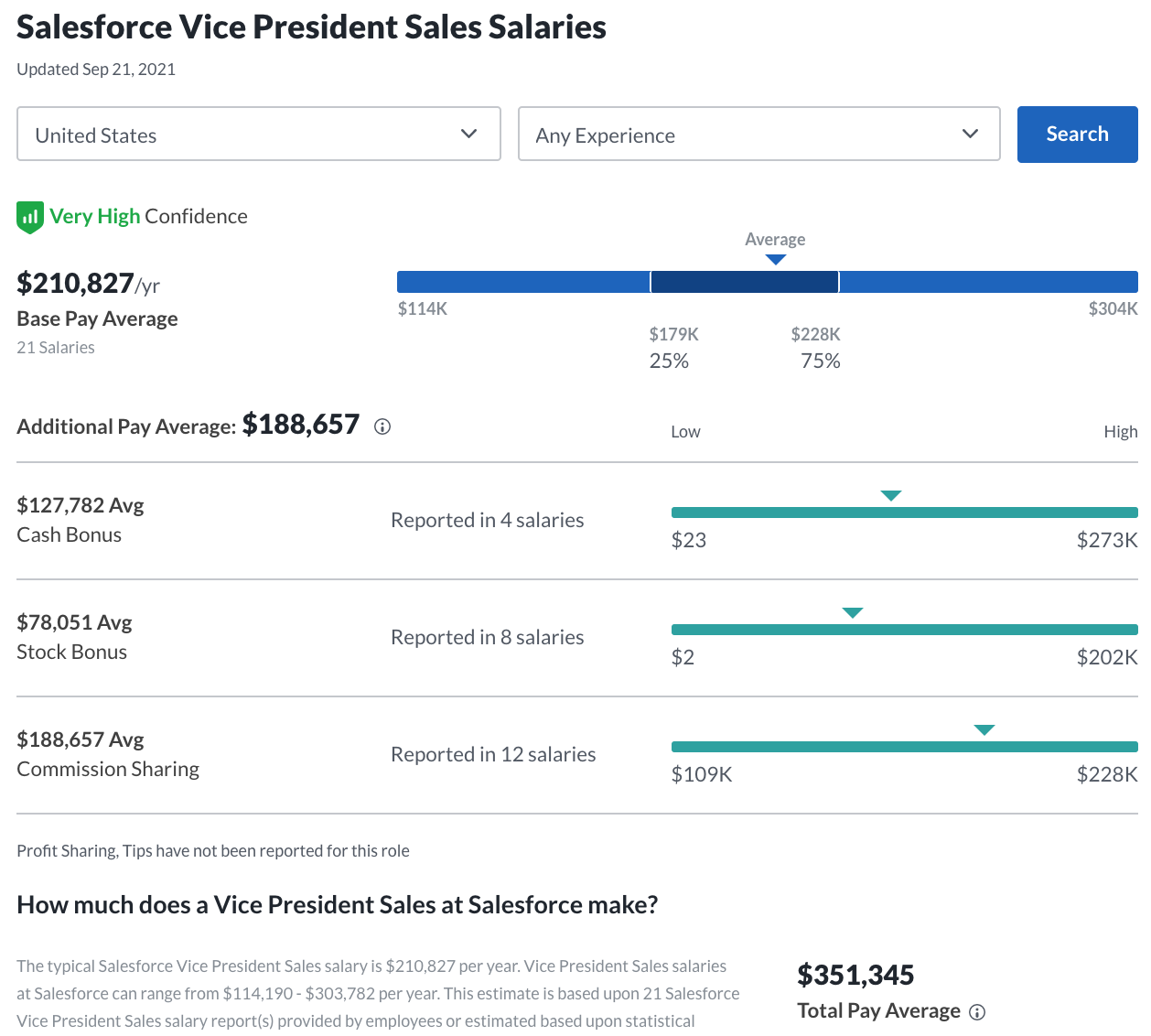
To give you something to look forward to, the average VP of Sales at Salesforce makes a total of 351,345/yr.
Solution Consultant/Solution Engineers
Solution Engineers, or consultants, are technically skilled representatives that help prospective buyers understand the value of a complex software product. These engineers assist another sales rep, typically an AE, and are not quota-carrying.
They’ll learn about the buyer’s situation, networks, and current software systems and figure out how their software solution can fit in and solve any pain points. They’ll then give technical presentations to decision-makers.
Here’s the breakdown of life as a software Solutions Consultant:
- Day-to-Day Responsibilities: Give presentations, conduct discovery about prospect’s challenges, find solutions, provide technical support to AEs, and answer technical questions from prospects.
- Average Earnings: $98,828/yr base salary. These reps can earn more in the form of bonuses or profit-sharing, but they don’t have commission plans since they’re not quota-carrying.
- Potential Career Paths: Could become a Senior Solutions Consultant and start assisting with larger deals, or could transition into Customer Success or Account Executive positions. You could also take all you’ve learned about the customer’s needs into the product department.
- Preferred Qualifications: Extensive product and technical knowledge, understanding of system interplay and integrations, background or degree in computer science or software engineering, and sales experience.
- Required Skills: High-level communication skills, computer skills, presentation skills, and attention to detail.
If you’re a technically gifted individual, the solutions consultant position might be a great fit for you.
Customer Success Manager (CSM)
A software CSM is in charge of managing and growing relationships with current clients, as well as onboarding and training new ones. They usually have a book of business of anywhere from 5 to 100 different clients, depending on the average size of each account.
Unlike AEs, CSMs are not typically quota-carrying, although they may still assist AEs in upsells or cross-sells to current clients.
Here is the big picture view of the life of a software industry Customer Success Manager:
- Day-to-Day Responsibilities: Answer client questions and address product issues, strategize with clients about how to get the most out of the software, assist with implementation, onboard new clients, facilitate upsells, and save distressed accounts.
- Average Earnings: $80,311 base salary. These reps can earn additional variable income in the form of bonuses or profit-sharing, but they usually don’t have commission plans since they’re not quota-carrying.
- Potential Career Paths: Could become the VP of Customer Success or manage a larger, more valuable book of business as a Senior Customer Success Manager. Or, they could switch over to sales or marketing. The paths are almost endless.
- Preferred Qualifications: A background in sales or customer service, experience saving accounts, and experience assessing customer success metrics to improve the process.
- Required Skills: Ability to become product experts, communication skills, relationship-building skills, crisis management tact, diplomacy, and sales skills.
Customer Success Managers are typically naturally skilled at handling people, no matter how difficult the personality. They know how to build connections, solve problems for clients, and use diplomacy and sales tactics when a customer is considering leaving. This is also a great position for any sales rep looking to take a break from the pressure of constantly hitting a quota.
Learn more about how much you can make as a CSM in our article on CSM earnings with regard to different locations, experience levels, locations, and industries.
Types of Software Companies
The software can help countless industries. This applicability has led to many types of software companies springing up, from HR software to education tech. Let’s briefly go through the main software company types to show you all of the opportunities out there.
Here are the most common types of software companies:
- Healthcare Software: Any software that assists and guides medical professionals in their treatment of patients. A common type is electronic health records that enable easy tracking of a patient’s history.
- HR Software: Helps HR professionals manage their many tasks like tracking attendance or staying in regulatory compliance. Examples include payroll tools, benefits administration software, and job applicant tracking systems.
- Education or K-12 Tech: Helps teachers and administrators provide the best education possible to their students. Categories include student information systems, learning management tools, and classroom management software.
- Construction Software: These tools help simplify the construction management process. They typically facilitate real-time online collaboration, project management and task tracking, and online document storage.
- Automotive Software: Helps automobile manufacturers streamline the production and design of new, innovative cars. A popular example is software used in self-driving cars.
- Real Estate Tech: Helps real estate professionals sell or manage properties. Listings software, property management software, and brokerage software are all subcategories.
- Cybersecurity Software: Helps companies protect against cyberattacks by improving the information security of a network or computer system.
- Financial Software: Handles storage and analysis of financial information. Ranges from personal finance solutions like budgeting apps to business financial software like business accounting software tools.
- CAD Software: Computer-aided design is software that helps designers improve productivity and the quality of their design. Also improves communication through automated documentation. It can assist anyone from civil engineers to consumer product manufacturers.
- ERP Software: Enterprise resource planning software helps organizations manage and automate daily business activities like accounting, risk management, compliance, and supply chain operations.
- Hospitality/Restaurant Software: Tools that help hotels, restaurants, resorts, and other hospitality businesses service their customers and streamline operations. Examples include tools that optimize hotel room assignment or manage housekeeping services.
- Logistics Software: Helps businesses manage the many moving parts of the production process like arranging for delivery of raw materials and shipping finished goods to retailers.
- IT Software: Helps IT professionals diagnose and troubleshoot technical problems at their business.
- Legal Software: Assists legal professionals by automating legal drafting, storing documents, managing contracts, appointments, and deadlines, or streamlining other day-to-day legal tasks.
With so many types to choose from, it can be hard to decide which industry is best for you. We recommend selling software in an industry that you understand or find interesting, as this will lead to better conversations with the decision-makers in the industry, which will, in turn, help your sales numbers. Plus, when you are curious about your industry, you’re less likely to burn out or get bored.
Companies That Are Always Looking for Software Salespeople
Some software companies are always on the hunt for quality sales talent to add to their seemingly always growing sales teams. Here are some of the best companies we recommend checking out if you want to work in tech sales.
IBM
International Business Machines (IBM) sells software that helps organizations in a wide variety of disciplines, from blockchain and cloud computing to IT management and Infrastructure. IBM’s software sales reps take home an average of $161,279 a year, making it a great place of work for those looking to earn big numbers.
Oracle
Oracle sells database software, cloud-engineered systems, and enterprise software solutions. It’s currently the third-largest software company in the world, and its headquarters is based in Austin, TX, a city bustling with new and innovative software companies. Oracle’s Account Executives make an average of $104,196 a year.
Salesforce
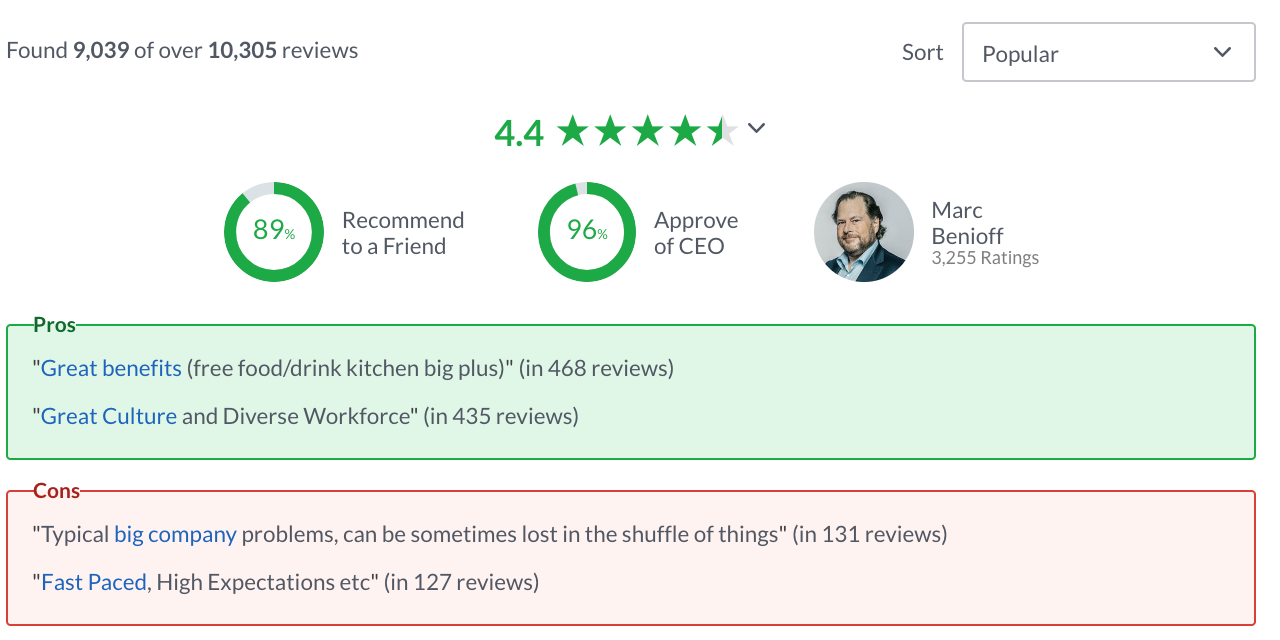
Salesforce sells a state-of-the-art customer relationship management system (CRMs) that is used mainly by mid-market and enterprise companies. Their CEO, Marc Benioff, is well-liked by his employees and was named the “innovator of the decade” by Forbes.
At Salesforce, a sales development representative can expect to earn $64,195/yr. However, when they learn and advance into the Account Executive role, they can make a comfortable 136,329/yr.
Regardless of pay, Salesforce is known as a great place to work and build your foundational skills as a software sales professional. Just look at the reviews from employees.
Dell
Dell, primarily a maker and seller of PCs, also offers software solutions for data center and cloud management, mobile workforce management, information management, and security.
Their Account Executives make $176,534 total pay a year, while their sales or solutions engineers average about the same, at $174,561/yr. The company also offers employees a flexible schedule and work-from-home opportunities.
UKG
UKG, Ultimate Kronos Group, sells human resources, payroll, and talent management software that enables businesses to streamline and automate their HR tasks. Sales Executives at the company earn an average of $196,904/yr, while Account Managers average $71,051, and Sales Directors $292,575/yr, according to Glassdoor’s data.
The company also boasts a solid rating of 4.1/5 as a place to work. Check out this review from a Business Development Manager:
Microsoft
The brainchild of Paul Allen and Bill Gates, Microsoft offers various operating systems and software for desktop computers that helps businesses increase productivity, visibility, and efficiency. Working for Microsoft means a chance to earn a high income, get great benefits, and work with talented individuals, however, you might have to sacrifice some work-life balance to do so. It might be worth it when its AEs make an average of $176,999 total pay a year. Also, check out its ratings by category.

SAP
SAP is a leading producer of ERP software that helps companies of all sizes increase their profits through effective data processing. The behemoth scores a 4.5/5 as a place to work, according to over 15,000 of its current and past employees.
Its Account Executives take home an average of $161,543/yr, while its VP of Sales earns a not too shabby $384,864/yr. Below are its scores, pros, and cons.
Workday
Workday is a leader in financial management and human capital management software. Its Account Executives earn a very high rate to sell this often complex software — $214,944/yr total. Although the leadership is considered exceptional, only 81% of employees would recommend working there to a friend.
HubSpot
HubSpot sells marketing automation and CRM software that helps businesses grow and track their client base. You’ve likely read their blog posts before. They dominate the results pages whenever you ask a question about marketing or sales.
An Account Executive at HubSpot is likely to earn $125,499/yr while a Senior Account Executive averages $158,309/yr. The company offers unlimited vacation time and other perks that make it a great place to grow as a professional while also enjoying your other interests and hobbies. They currently have open sales jobs across the globe:
Best Cities for Software Sales Jobs
When people think of tech hubs they typically think of San Francisco and New York City. But, over the past decade, numerous other cities have started to attract software companies and startups. So, we’ll take a look at the cities offering the most tech sales positions.
First, though, it’s important to note that many of the top B2B software companies are now offering remote sales positions, meaning that, regardless of the company’s location, their sales reps can work from anywhere — their home in another state, a local coffee shop, or a co-working space like WeWork.
Of course, if you enjoy the camaraderie that comes with sales culture in the office, most companies offer that option as well.
Here are the top cities for software sales jobs and some great companies with offices in the area:
- Dallas: Intel, Legalinc, and McAfee.
- Austin: Atlassian, GoDaddy, and LeadDNA.
- Chicago: Sprout Social, Upwork, and Lever.
- Boston: Buildium, HubSpot, and One Door.
- Denver: Microsoft, NetSuite, and TrackVia.
- Detroit: Adobe, Brightly, and Logicdrop.
- Pittsburgh: Net Health, SAS, and Target Freight Management.
- Miami: Engage, Paradox, and Userlytics.
- Philadelphia: Odessa, Guru, and The Neat Company.
- Raleigh: Bandwidth, Red Hat, and Pendo.
- Toronto: Payforpitch, Elastic, Adobe.
If you’re interested in moving to one of these fun and cultured metropolitan areas, check out the above-listed companies and see if they’re hiring, or, head over to the Salestrax job board and filter by location to find tech sales jobs in your chosen city:
Bottom Line: Software Sales is The Place to Be
Software sales reps are thriving. They enjoy high earning potential, flexible working hours and location, and a perfect environment to grow their sales skills and advance through the ranks.
Plus, once you work in tech sales, many other opportunities open up for you, whether that means transitioning into finance or consulting, or even starting your own business. Employers value experience in software sales. You’ll have practiced problem-solving, relationship building, and working with a complicated product.
To learn more about the tech sales journey, check out the Salestrax.com blog, which is dedicated to helping software salespeople land the perfect job for them.